The research focuses on the overfitting problems caused by high-dimention and limited samples. From the view point of semi-superivised learning, we adopt fully constraint sparse representation to build sparse graph, and design sparse graph regularization based semi-supervised classification method. In addition, active learning is introduced to improve the classification performance and convergence rate. To this end, a novel sparse graph regularized active semi-supervised learning method is proposed. To better leverage the spatial information, a Gaussian kernel based weighted adaptive spatial modeling method is introduces into the model, leading to more discriminant representation. Those research studies were published on ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, and IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, etc.

Associate Professor Huang Guojiao first introduced the research background and research significance of the microseismic location that plays an important role in hydraulic fracturing analysis (an important production increase measure in the development of unconventional oil and gas resources), and emphasized the importance and necessity of this research. Then, by analyzing and summarizing the current research status of this method by domestic and foreign scholars, the research question is drawn, that is, to reduce the microseismic location errors, it is necessary to develop a method that simultaneously updates the velocity model and locates events in space and time. Then, the principle of the method is explained in detail, including the improved shortest path method based on interface elements and the partial derivative of Thomsen parameters, layer interface depth, source space coordinates, and onset times are derived. The difficulties and innovations of the method are pointed out. Finally, a numerical simulation experiment of a layered TI medium model is used to verify the effectiveness and correctness of the algorithm. The numerical examples show that when the ray angle coverage is good, the proposed algorithm can be used to invert the anisotropic velocity model (Thomsen parameters and interface depth for each layer) and locate the microseismic sources and their onset times, simultaneously. And it is not so sensitive to random noise, which is beneficial for the actual engineering applications. However, in actual production, there are other factors such as uneven stratum and low data signal-to-noise ratio. Therefore, in future research, it is necessary to combine actual data and site geological conditions to apply and test the reliability and robustness of this method. Thereby and further improve the actual positioning accuracy.

At 25th September, Dr. Fei Xue gave an academic report entitled “Geochronology, petrogenesis and tectonic significance of the Laiyuan magmatic complex in the central North China Craton” in Room 208, Duxue Building. He first introduced the meaning of petrology, scientific significance and basic research methods of petrology with vivid examples. He took the Laiyuan complex from the central North China Craton as an example to explain how to conduct petrological studies. Here, he presented new petrological, mineral chemical, geochemical, geochronological and isotopic data to reveal the spatial, temporal, petrogenetic and tectonic linkages between different magmatic suites and to establish an integrated petrogenetic model for the Laiyuan complex, and furthermore to assess the craton destruction mechanism and lithospheric evolution in the central NCC. He explained the research vividly attracting the attention of the teachers and students present.

On September 27, 2020, Dr. Ding Yuan of our college gave a wonderful report entitled Research on GIS Spatio-temporal Data Modeling and Simulation Method in Smart City to all teachers and students.The report expatiated on the simulation method of urban expansion in the smart city. A whale optimization algorithm (WOA)-based CA (WOA-CA) model to simulate urban expansion was introduced in the report. The WOA-CA model was used to simulate the urban expansion of Guangzhou from 2000 to 2010, and the obtained simulation results had high similarity to the real situation. The comparison experiments show that The WOA-CA model has better simulation accuracy.In the section of discussion and exchange, Dr. Ding Yuan answered the questions of teachers and students in detail, and launched a heated discussion and exchange on some related scientific issues. The teachers and students who attended the meeting benefited a lot.

On September 27th, 2020, Zheng Xiangtian, a postdoctoral fellow from the Hohai University made an academic communication through webinar conference. Dr. Zheng gave a wonderful report entitled Matching and Integration of Slope Deformation monitoring Radar to the teachers and students in our school. He summarized the research progress of slope deformation monitoring radar and introduced the frontier slope radar systems and the specific requirements of matching and integration. Then, the improved methods based on rigid body transformation and the mismatched correction method based on affine transformation were introduced In view of the deficiency of slope radar image and terrain data matching and fusion technology, and the practical effect of the method is demonstrated by combining the simulation experiment and the actual application of slope radar deformation monitoring. Finally, in the discussion after the report, Dr. Zheng gave detailed answers to the questions raised by the teachers and students attending the network meeting and discussed with professor Su Hongjun the demonstration application of the method shown in the report in the localized slope radar system. The teachers and students at the meeting discussed the contents of the report.

On September 27, 2020, Professor Hongjun Su of the Department of Surveying and Mapping Science and Engineering gave a webinar entitled Ensemble Learning for Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Classification with Collaborative Representation. Some faculty, graduate and undergraduate students of the School of Earth Science and Engineering attended the presentation.In this report, with the support of collaborative representation and ensemble learning, three effective ensemble learning algorithms are proposed from sample layer, feature layer and classifier layer, respectively. In addition, the report also introduces three research directions for hyperspectral remote sensing ensemble learning classification.In the discussion and interaction, Professor Su answered the questions raised by the teachers and students. The report was rich in content and novel in viewpoint. Through this academic exchange, we have a further understanding for hyperspectral remote sensing image lassification.

Firstly, Dr. Zhu explained the reason why there are few researches on the stability of anti-dip slope at home and abroad by expounding the definition of anti-dip slope. Then, taking the case of changshanhao mining area in Inner Mongolia as an example, the physical model experiment of toppling failure of anti-dip slope was carried out, and the toppling failure characteristics and mechanism of anti-dip slope under excavation were explored. According to the failure characteristics of the anti-dip slope, the negative position's ratio (NPR) anchor cable was proposed to control the anti-dip slope, and the control mechanism of the NPR anchor cable on the failure of anti-dip slope was obtained through the model experiment, which provided a new way for controlling and monitoring the toppling failure of similar anti-dip slope failure. The content of the academic report was rich and wonderful, and the logic was strict, which had aroused heated discussion between teachers and students.

Grouting is a common method used to fill rock joints to improve the stability and integrity of rock masses in geotechnical engineering, and the filling has been observed to have an effect on cracking behaviors and mechanical properties. Exploring the grouting mechanism and physical and mechanical properties of fractured rock masses under the influence of multiple factors is of great significance for evaluating the stability of geological bodies. This report introduces cracking behaviors and mechanical properties of rock masses containing flaws grouted with different grouting materials. Epoxy resin and cement paste were chosen as grouting materials, uniaxial compressive tests were conducted on the specimens containing single grout-infilled flaw having different inclination angles. Experimental results show that grouting materials and flaw inclination angle have a significant influence on the uniaxial compressive strength and failure mode of rock-like specimens. The reinforcement effect of epoxy resin is better than that of cement paste, epoxy resin can effectively eliminate the stress concentration of the tips of the grout-infilled flaw. This study provides a theoretical frame for analyzing the influence of grouting materials and the inclination angle of flaw on the strength of rock mass in engineering projects.

On the afternoon of September 27, 2020, Dr.Wei Yunbo from the School of Earth Sciences and Engineering of Hohai Universitygave an online academic report entitled The experimental and theoreticalstudy of air-water displacement in the unsaturated zone. This report isthe thirteenth report of the Lecture series “Lecture on Earth Science”organized by the School of Earth Sciences and Engineering, and it is also partof the academic activities celebrating the 105th anniversary of HohaiUniversity.This lecture mainly introduces the recentresearch results and key issues encountered by Dr. Wei. In the lecture, Dr. Weisystematically explore the mechanisms of air-water displacement and their effectson the water content/infiltration rate in unsaturated zone. Experiments,analysis and numerical simulations for different unsaturated zone processes(drainage-imbibition processes, rainfall infiltration processes) are introducedin the lecture. After the lecture, the teachers and students who participatedin the meeting had an in-depth discussion on related issues with Dr. Wei. Theparticipants benefited a lot from it, and the response was very good. Theconvening of this academic report has laid a good foundation for futurescientific research cooperation between teachers and students.

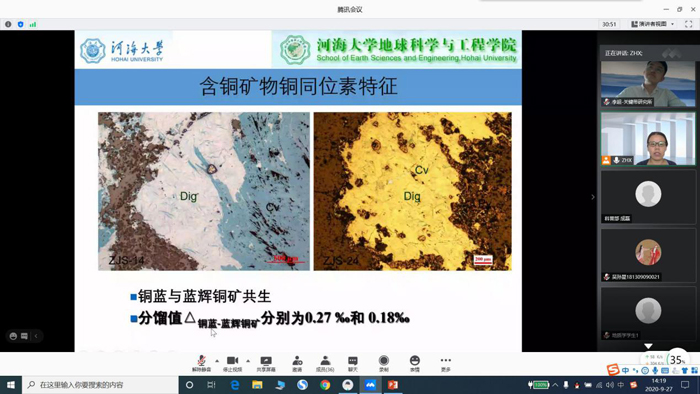
In the afternoon of September 27th, 2020, Associate Prof. Zhao Haixiang gave a lecture titled “Copper isotopic characteristics of Cu-bearing minerals from Zijinshan ore field, Fujian province: implications for ore genesis”. First of all, she introduced the definition and research progress on copper isotope. After the geological background introduction, she showed the copper isotopes of covellite and digenite from Zijinshan ore field. Finally she came to the conclusion that Zijinshan and Wuziqilong deposits are of hydrothermal origin, not of supergene genesis.
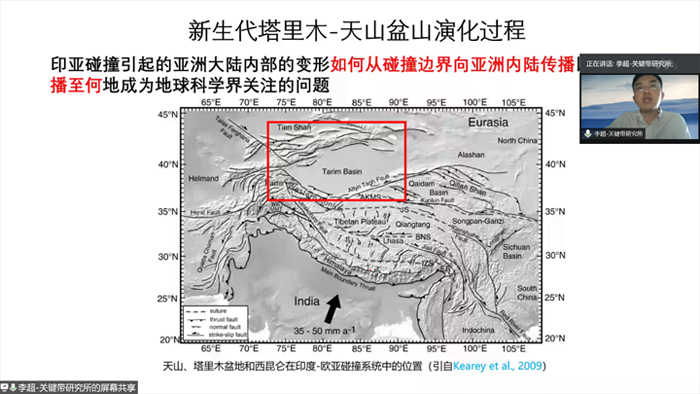
In the afternoon of September 27th, 2020,Dr. Chao LI gave a lecture titled “Reconstruction and numerical simulation ofthe migration and subsidence history in the foreland basins of the eastern TianShan in the Cenozoic”, through web meeting. Dr. LI first introduced the meaningof Tectonics, scientific significance and basic research methods of Tectonicswith examples, and emphasized the significance of the research of mountain-basincoupling in the Global Tectonics. He took the Cenozoic southern Tian Shanforeland basin as an example to explain how to conduct the mountain-basincoupling study. In his study, the uplifting process of the eastern Tian Shan is rebuildingbased on deciphering the subsidence and migration history of the foreland basin,by seismic profiling and numerical modelling.Heexplained the research vividly attracting the attention of the teachers andstudents present.
Dr. Lifang Zou gave a speech on numerical analysis on permeability anisotropy of columnar jointed rock masses (CJRM) under different stress conditions on Sep. 27th 2020. CJRM are well developed at the right bank of Baihetan hydropower station. As they have a very special structure, they are of strong mechanical anisotropy and hydraulic anisotropy. Coupled hydro-mechanical analysis is of vital importance to the hydraulic investigation of the underground cavern excavation in the abutment slope. Firstly, equivalent hydraulic REV of the CJRM is obtained by using two dimensional numerical analysis. It is found that CJRM have an obvious hydraulic anisotropy. Two principal permeability coefficients and the direction of the maximum principal permeability coefficient are obtained. Secondly, the effect of burial depth, principal stress ratio and principal stress direction on the permeability of CJRM is investigated by 2D discrete element method. It is found that different stress conditions have an obvious effect on permeability anisotropy of CJRM. Thirdly, hydro-mechanical coupling analysis is conducted on excavation of the tailrace tunnel in CJRM by using 2D equivalent continuum media method and discrete element method. Anisotropic hydraulic characteristics of the surrounding rocks are obtained under the condition that the direction of the principal stress is not in accordance with the direction of the principal permeability. Hopefully the work can provide a reference to the project design of Baihetan hydropower project.
